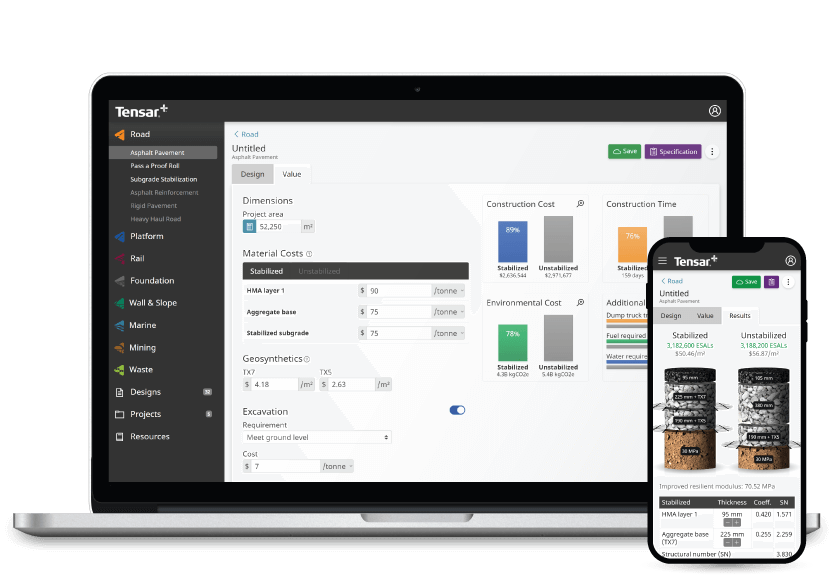
Rail
Helping rail authorities stretch budgets further
Rail Authorities across the globe face the monumental task of building and maintaining the railway networks that move passengers and freight across nations and continents. Rail Engineers designing new railway seek to deliver safer, better, longer-lasting railways more economically, more sustainably and with greater climate resilience. Those responsible for maintaining existing rail networks face a widening gap between the needs of a deteriorating network and squeezed maintenance budgets.
With materials and labour costs continuously rising and the scope of their responsibilities consistently expanding, how do rail authorities keep up? Tensar helps railway authorities stretch trackbed, earthworks, and bridgeworks budgets further, by using our proven technologies - supported by Tensar expertise and software.

Railway Embankments
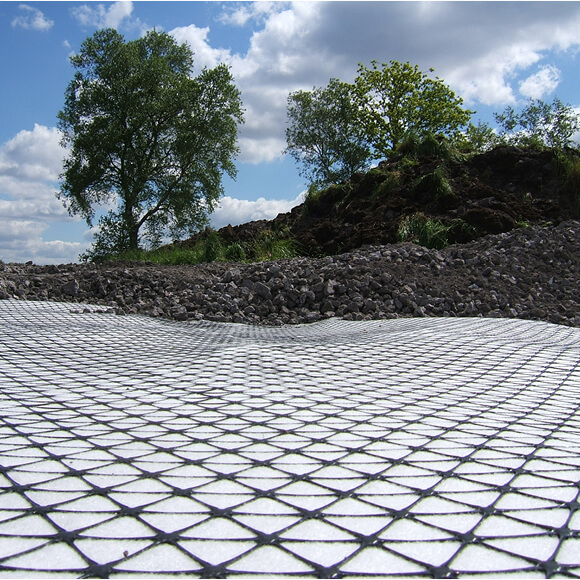
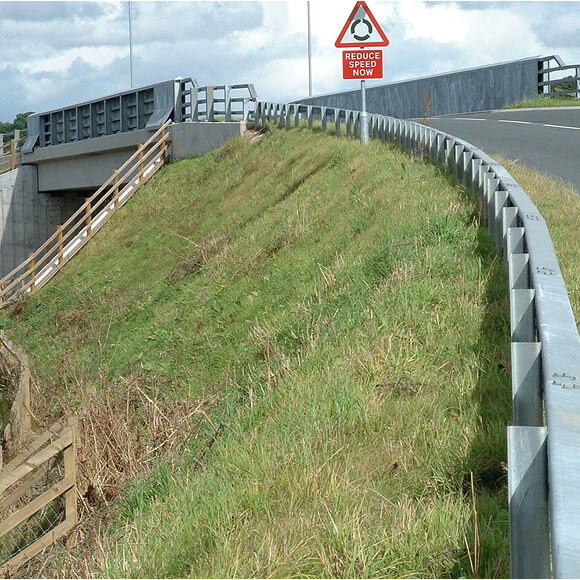
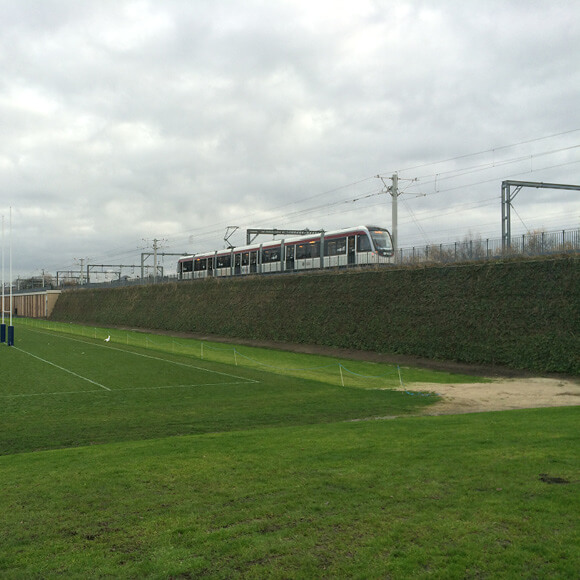
Rail embankments allow rail tracks to be established at a raised level, ensuring the train can pass easily over the terrain, especially where there is an incline across the landscape. The construction of optimal railway embankments also facilitates critical railway drainage, settlement and erosion control so the track is viable for years to come.
The aim of incorporating geotechnical engineering solutions into railway embankments is to produce them with greater resilience, whilst reducing costs and carbon emissions. By incorporating Tensar geogrids into the steep-slope rail embankments, the maintenance lifecycle is significantly improved, risk of erosion is reduced and settlement is controlled. They can also meet aesthetic requirements with a number of facia options available such as naturally vegetated slopes.
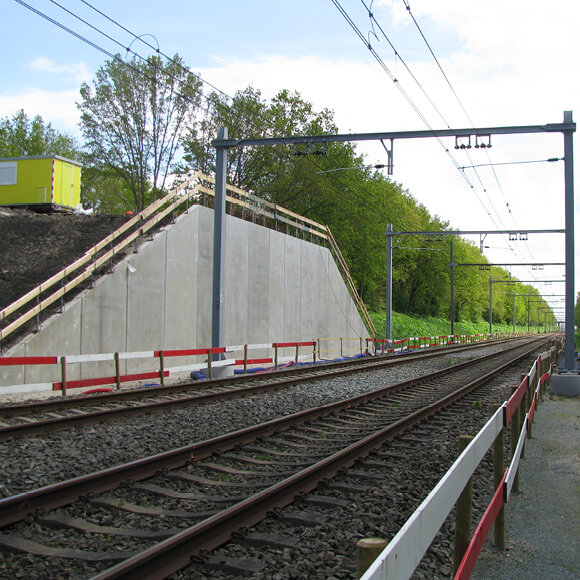

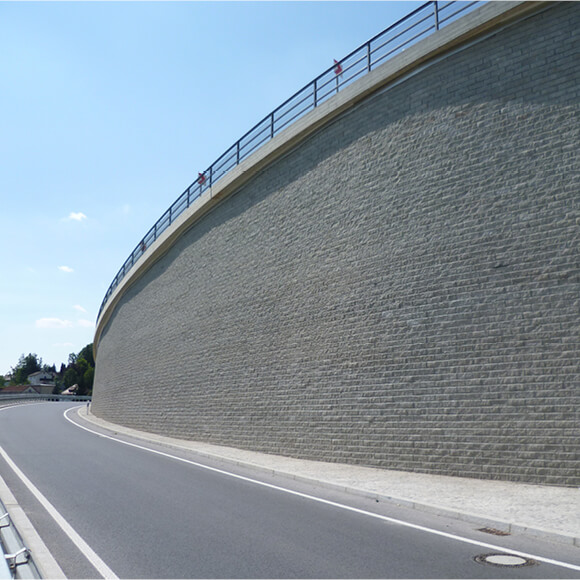
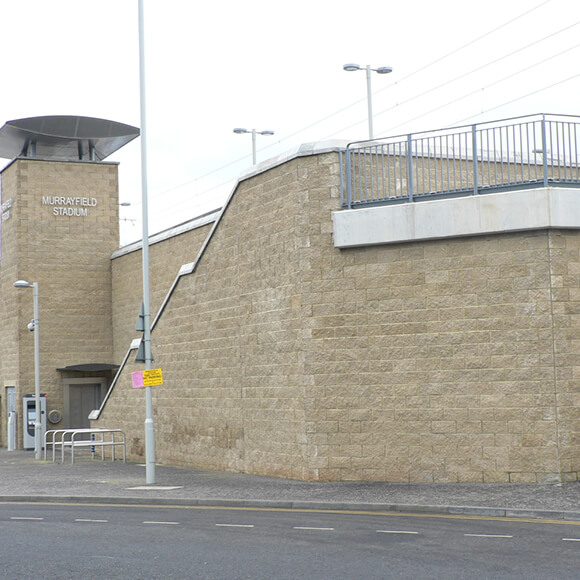
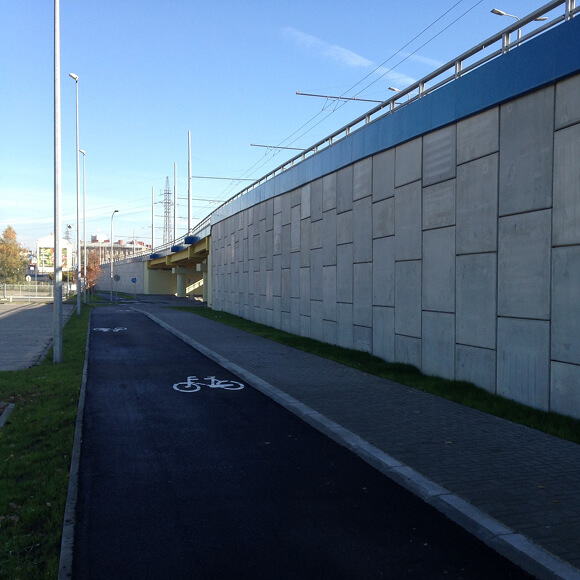
Railway Retaining Walls
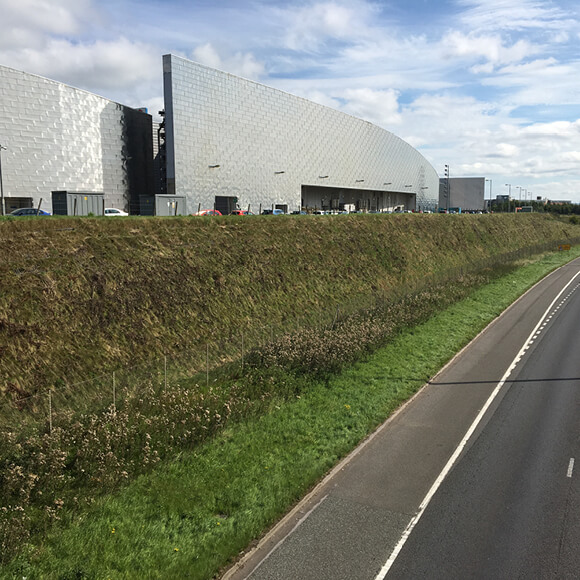
Railway retaining walls are fundamental to rail networks, both protecting rail tracks at a lower level, whilst also supporting elevated rail tracks such as those on embankments. Retaining walls on railway lines can be especially effective where space is restricted, allowing the structures footprint to be minimised in areas such as high-density urban cities.
Engineering railway retaining walls can be particularly difficult as rail loads differ massively to that of highways, and often require near vertical sloping soil. Therefore using retaining walls with superior structural integrity, such as TensarTech Earth Retaining Systems, allows Rail Authorities to choose a rail retaining wall that can maximise the land available, reduce construction times and utilise site-won materials.
Need a retaining wall or slope design for your rail project?
Tensar’s design team can produce a free of charge “Application Suggestion” to illustrate what Tensar can achieve and how much value can be added to your project.
Request Design Assessment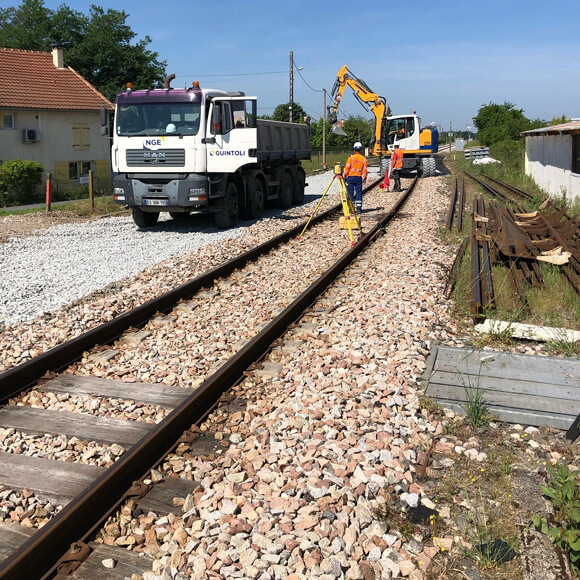
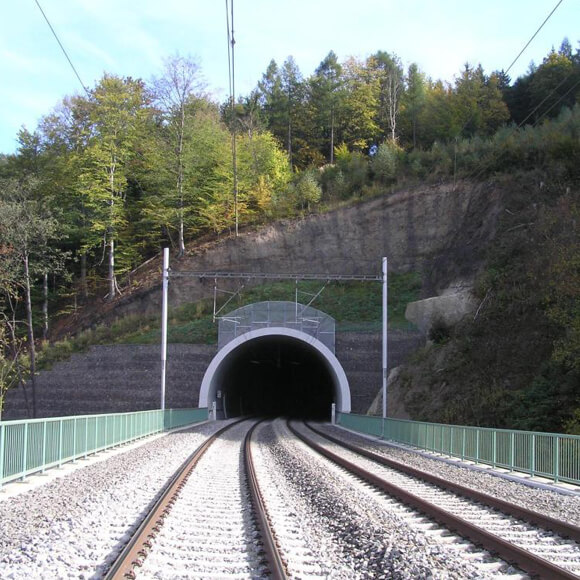
Rail Track
What if you could design higher performing trackbed more sustainably and with greater resiliency - without increasing costs? What if you could extend trackbed service life or greatly extend the periods between routine maintenance?
The rail track is the primary focus of a railway, but it is supported on major earthworks, embankments and bridgeworks. Structural and geotechnical engineers building railway infrastructure are faced with the same pressures: to deliver more for less. They also seek to design more economically, more sustainably and with greater resilience. The goal is to construct railway embankments with a reduced footprint, more quickly and with reduced carbon emissions or for a rail bridge or over bridge decks to be constructed bank seats bearing directly on lower-cost reinforced soil abutments using re-cycled fill. Tensar has proven innovative solutions for trackbed, earthworks, and bridgeworks - supported by Tensar expertise and software.
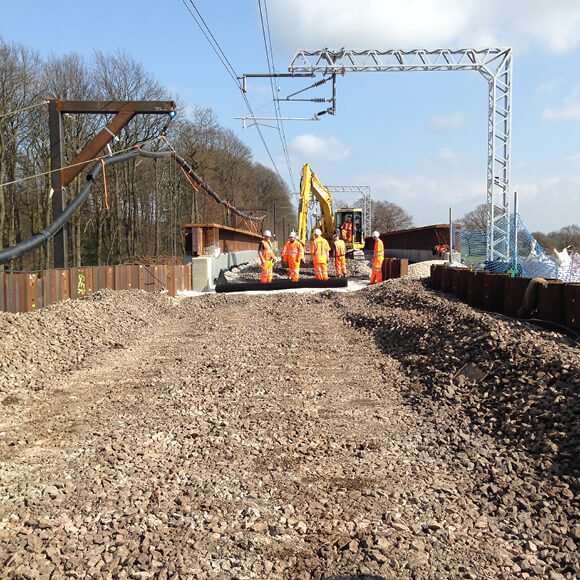

Even Better Value
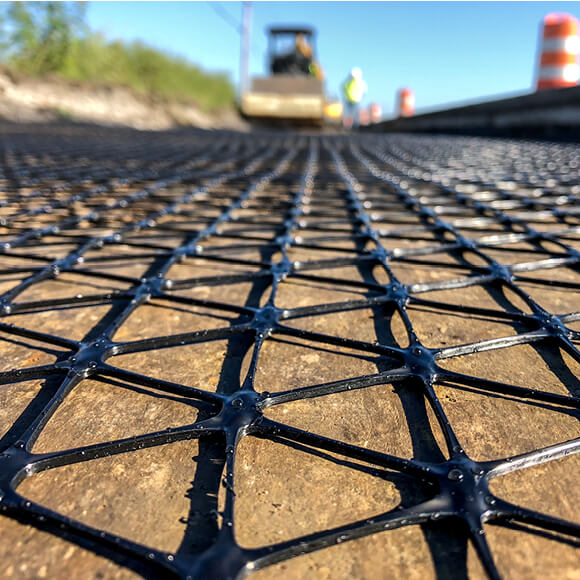
An efficient rail network must maintain design speeds and minimise service disruptions for major maintenance operations. The quality and durability of the trackbed are critical, both in determining safe operating speeds and in minimizing maintenance related disruption.
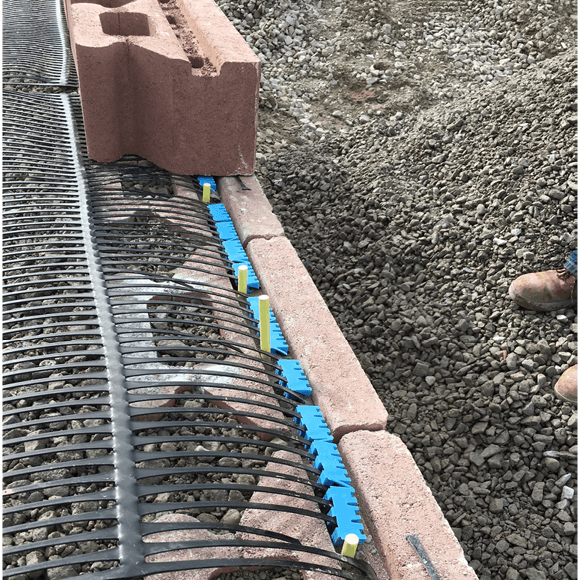
In new track and track reconstruction works the bearing capacity and stiffness of the trackbed foundation can be improved by incorporating Tensar stabilisation geogrids into the sub-ballast layer. In ballasted track, the time between necessary tamping maintenance can be significantly increased by incorporating Tensar stabilisation geogrid in the base of the ballast layer. Ballast degradation and track settlements are reduced, maintaining track speed and extending maintenance cycles.
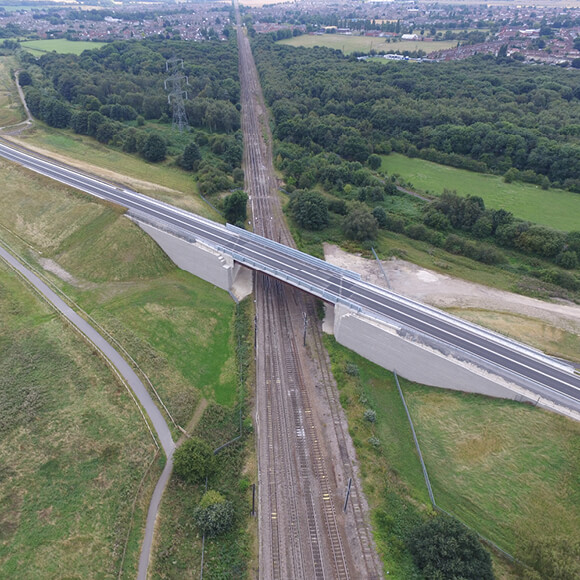

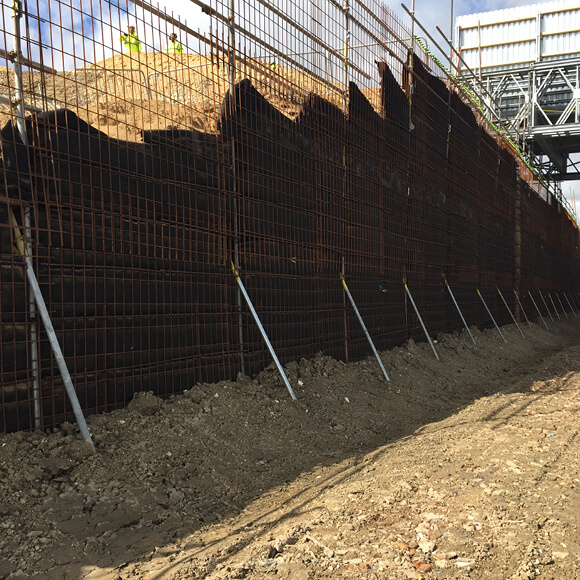
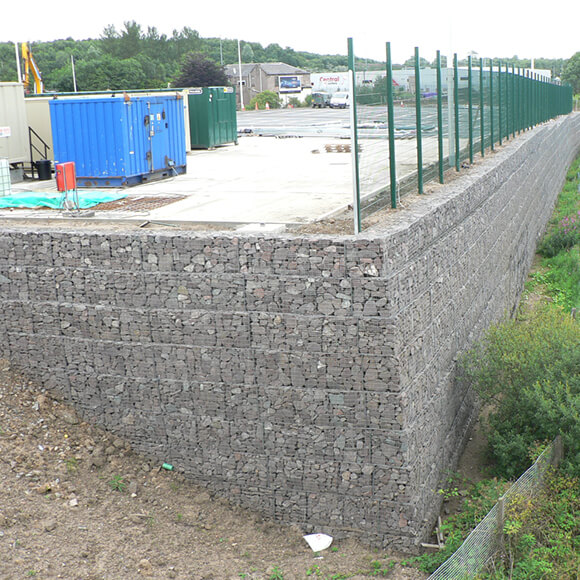
Earthworks and Bridgeworks
Almost all rail projects involve the construction of retaining walls, road embankments, bridge abutments, and other features. Tensar has a range of TensarTech earth retaining systems for retaining walls, steep embankments and bridge abutments. These solutions offer major cost advantages and construction programme advantages over alternative construction methods. They also enable use of re-cycled or site-won fill materials to keep down costs and minimise local impact.
Additionally, Tensar has innovative solutions for the construction of embankment foundations over weak soils. These can be quicker to construct, with a reduced land take and controlled settlements.